The Recipe to a Healthy Heart:Your Guide to Preventing Heart Disease
Sure, the taste of food is important, but do you know how your diet impacts your heart? Many foods contain hidden ingredients that negatively impact...
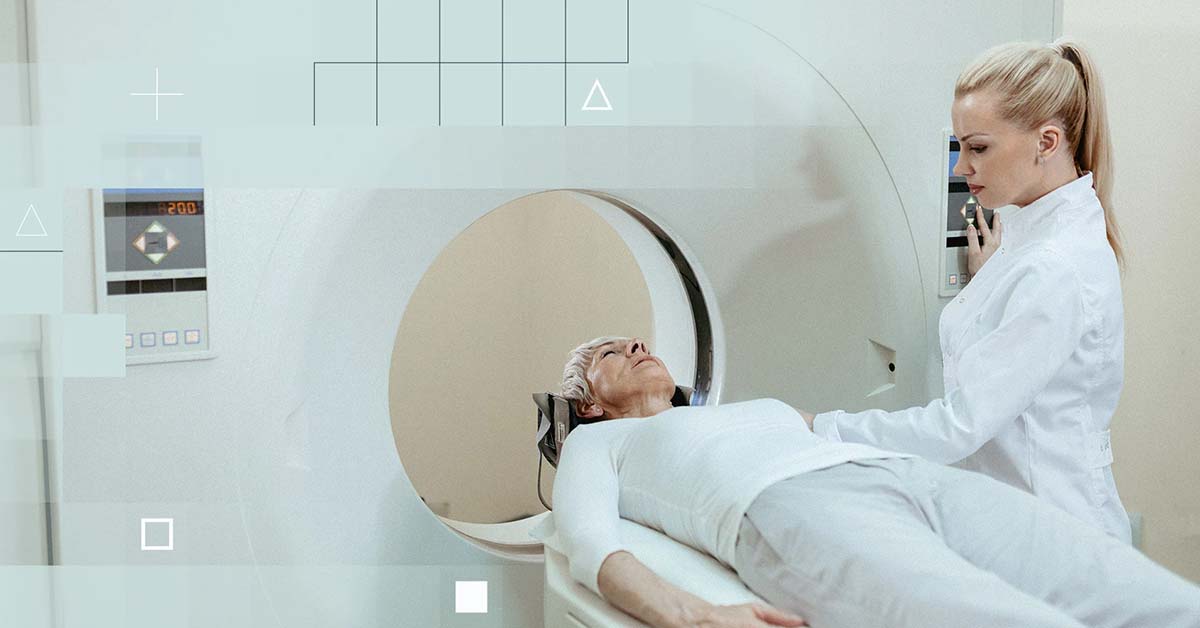
Cleerly makes early detection of heart disease risk possible through our AI-enabled analysis of coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) imaging that guides physicians towards creating personalized and preventive treatment plans for patients. To help providers and patients achieve the benefits of our new standard of care, we’ve provided details on the CCTA scan and Cleerly analysis process below.
A CCTA is a heart-specific diagnostic imaging scan that helps determine if plaque buildup has narrowed the coronary arteries, the blood vessels that supply the heart, which can lead to coronary artery disease (CAD). Computed tomography is more commonly known as a CT or CAT scan. Like traditional x-rays, it produces multiple images or pictures of the inside of the body.
The Cleerly coronary analysis is a thorough evaluation of the presence, amount, and type of plaque in the heart’s arteries based on a CCTA study. Images captured in the CCTA scan are processed by Cleerly software - a set of artificial intelligence-based algorithms - and translated into measurements and reports for review by the patient’s physician. The results of the Cleerly analysis give a patient and their physician a comprehensive understanding of the patient’s current state of cardiovascular disease for reference in the patient’s ongoing heart health and treatment.
During the CCTA scan, x-rays pass through the body and are picked up by special detectors in the scanner. Typically, higher numbers (CCTA is best at 64 or more) of these detectors result in clearer final images. The information collected during the CCTA scan is used to identify the coronary artery anatomy, plaque, narrowing of the heart vessel, and, in certain cases, heart function.
Patients undergoing a CCTA scan receive an iodine-containing contrast material as an intravenous (IV) injection to ensure the best possible images of the heart blood vessels. The contrast material is used to clearly define the blood vessels being examined by making them appear bright white. Due to the iodine contained in the contrast, patients are screened for chronic or acute kidney disease.
Patients may feel warm or flushed as the contrast is injected. They may have a metallic taste in their mouth or feel a need to urinate. These sensations will pass as they are only side effects of the contrast injection, and they subside quickly.
Including all preparations, the CCTA scan usually takes about 15 minutes if the heart rate is slow and steady. An intravenous (IV) line is inserted to administer contrast material during the procedure. The CT scanner projects special light lines onto the patient to ensure they are in the correct position on the scan table before conducting the scan. Patients may be asked to hold their breath during the scan for high image quality.
If medications are given to patients, blood pressure should be taken before, during, and following the scan. After the CT scan, the intravenous line can be removed and patients can return to their normal activities.
Cleerly analysis of the CT scan is completed in less than four hours. Clinical insights from the analysis are used to create personalized reports for patients and providers. Reports include an interactive, web-based summary and details of our AI-based plaque quantification to help providers translate clinical data for personalized CAD diagnosis and treatment.
Cleerly recommends physician and technologist training, proper patient screening and preparation, and use of prospective gating for accurate analysis. To learn about these and other best practices for performing a successful CCTA scan to ensure the highest level of image quality for analysis, subscribe to our webinar series.
Cleerly’s quantitative outputs have been validated in a series of six multicenter clinical trials, which we call the CLARIFY trials. These include validation against expert level 3 clinical readers, quantitative coronary angiography (QCT), intravascular ultrasound (IVUS), optical coherence tomography (OCT), near field infrared spectroscopy (NRIS), and invasive fractional reserve (FFR). These are the current gold standards for heart disease evaluation.
For more information on our new standard of care, visit our Cleerly Science page.
Want to learn more about Cleerly?
Connect With Us

Sure, the taste of food is important, but do you know how your diet impacts your heart? Many foods contain hidden ingredients that negatively impact...

As we reach the end of 2023 and yet another remarkable year at Cleerly, it’s a great opportunity to reflect on all we’ve accomplished and begin...

Cleerly has had a busy few months – attending conferences, panel sessions, and winning awards as we all work together to achieve our mission of a...

Findings from Cleerly's groundbreaking echo the recent American College of Cardiology guidelines on the use of CCTA for non-invasive heart disease...

Heart disease is the cause of death for 700,000 Americans1 and nearly 17.9 million people worldwide every year.2 While some of these individuals...

Last week, our team at Cleerly had the opportunity to take part in a gathering of impassioned cardiac computed tomography (CT) leaders at the Society...